Health Vectors
1st Floor
966, 27th Main, 8th Cross
Sector 1, HSR Layout
Bangalore 560102
(Behind Pai International)
What is Zinc? What role does it play?
Zinc is a trace mineral, meaning that the body only needs small amounts. Zinc is needed for many of the chemical reactions which are going on inside us all the time at micro-level.
Zinc is also needed for:
*Our immune systems to work well to fight off infection.
*Healing of wounds.
*Growing.
*Building the proteins and molecules which are the basis of all our cells.
*Taste, smell and good vision.
Sources of Zinc
Zinc is readily available in many foods including:
*Red meat.
*Chicken and other poultry.
*Seafood, particularly oysters (which are loaded with zinc), crab and lobster.
*Nuts.
*Grains, beans, lentils and split peas.
*Spinach.
*Dairy products - milk, yoghurt, cheese.
*Fortified breakfast cereal.
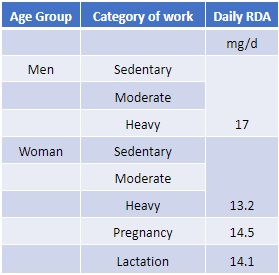
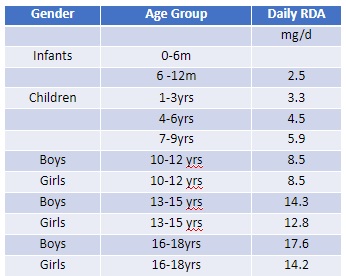
Recommended Dietary Allowance
Zinc Deficiency Symptoms
Zinc is used by your body in cell production and immune functions. Zinc is an essential part of growth, sexual development, and reproduction.
Symptoms of zinc deficiency tend to be linked to the roles that zinc performs in the body. Some of the most common zinc deficiency symptoms include:
*appetite loss
*slower than expected growth
*poor immune system function

Zinc Deficiency Symptoms
Severe zinc deficiency can cause even more concerning symptoms. Examples include:
*delayed sexual maturity
*diarrhoea
*eye and skin lesions
*feeling lethargic
*funny-taste sensations
*hair loss
*poor wound healing
*unexplained weight loss
Men and boys can also experience impotence and hypogonadism, which is when a male’s body does not produce enough testosterone.
Screening for zinc deficiency
Zinc is distributed in trace amounts among the cells in your body, making it difficult to detect zinc deficiency through a simple blood test.
In diagnosing a zinc deficiency, a doctor will need to take a full health history.
They will ask questions about your dietary intake.
If you do not take in enough calories daily or eat enough of a variety of foods, it is possible a zinc deficiency could be an underlying cause.
Causes of zinc deficiency
The chief causes for zinc deficiency include;
*Not consuming a diet rich in zinc.
*Having a chronic health condition like kidney or liver disease, chronic diarrhoea etc.
*Losing excess amounts of zinc from the body, due to poor absorption.
Other causes of zinc deficiency can include medical conditions like cancer, diabetes, pancreatic disease etc.

Risk Factors for Zinc Deficiency
The following individuals are at risk of developing zinc deficiency;
*People with gastrointestinal diseases that causes malabsorption of zinc from the diet.
*Vegetarians are at risk as the bioavailability of zinc from vegetarian diets is lower than from non-vegetarian diets.
*Pregnant women are at risk partly due to high fetal requirement of zinc.
*Alcoholics have low zinc status because ethanol consumption decreases intestinal absorption of zinc and increases urinary zinc excretion.
Treatment of zinc deficiency
You may need to increase your intake of zinc by getting more of it in your diet. Include in your diet zinc rich foods like red meat, chicken, shellfish like crabs, beans, dairy products, nuts etc.
If you have a condition that interferes with your ability to absorb zinc from foods, you may need to take supplements. Be sure to discuss these with your doctor and take them as recommended.

Excess zinc
The most common cause of zinc excess is taking too many zinc supplements. It is important not to take more than the advised dose. A number of different symptoms can occur if you have too much zinc in your system. For example:
*Tummy (abdominal) pains
*Diarrhoea
*Feeling sick (nausea)
*Being sick (vomiting)
*Headaches
*Tiredness
*Dizziness
The treatment for zinc excess, poisoning or toxicity mostly involves removing the source of zinc excess and then treating the symptoms until the zinc level settles back down.
Disclaimer: The advice provided is intended for informational purpose only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Consult with your doctor if you’re seeking medical advice, diagnoses, or treatment.